When used interchangeably, students get confused about what is the difference between curriculum and syllabus. Check out this article to clear all your doubts regarding the differences between 'syllabus' and 'curriculum'!
- Difference Between Curriculum vs Syllabus: Overview
- What is a Curriculum?
- What is a Syllabus?
- Difference Between Curriculum and Syllabus: Key Pointers
- Difference Between Curriculum and Syllabus: Developing a Syllabus
- Difference Between Curriculum and Syllabus: Designing a Curriculum
- Relationship Between Curriculum, Syllabus and Textbook
- Faqs
What is the difference between curriculum and syllabus: Curriculum and syllabus are two important terms that students come across in their education journey. The main difference between curriculum and syllabus is that a particular subject's syllabus is a part of a course or curriculum . A curriculum is a combination of the syllabus of all subjects, course design, class timetable, and lesson plans for a subject. While the syllabus outlines the topics and concepts to be covered, the curriculum encompasses how a particular subject or course will be taught. Often, these terms are used interchangeably, but they are fundamentally different. Understanding what is the difference between syllabus and curriculum provides a more detailed insight into the structure of an academic program. Let's delve into the discussion of curriculum vs syllabus and explore their key differences.
Also Read:
Difference Between Curriculum vs Syllabus: Overview
The curriculum includes all the content outlined by an education board for a specific course over a set period. On the other hand, the syllabus provides a summary of the various topics or units that will be taught within a specific subject or discipline under that particular course. If you are confused about what is the difference between curriculum and syllabus, check out the following table.
Point of Differences | Curriculum | Syllabus |
|---|---|---|
Definition | A curriculum comprises the courses and content provided by an educational institution. | A syllabus is a detailed list describing the subjects to be taught in a class, such as chapters to be covered. etc. |
Scope | The whole educational program includes various courses, subjects, and their connections. | It concentrates on an individual course or subject within the larger curriculum. |
Settings | It is not easy to make adjustments to the curriculum. | The syllabus can be easily adapted according to the specific requirements of each class. |
Content | The curriculum includes information about courses, goals, methods, and more. | The syllabus lists topics to be covered and provides details about assignments, assessments, and other specifics. |
Long-term vs. Short-term | Concerns long-term educational objectives and learning outcomes spanning an extended period, often years. | Relates to short-term instructional plans, typically for a single academic term or semester. |
Examples | A class 1 school curriculum details the subjects (such as math and science) and learning objectives for each grade level. | A syllabus for a class 11th and 12th Chemistry subject provides information about the topics, readings, assignments, and assessment methods specific to that class. |
What is a Curriculum?
The curriculum serves as the ultimate manual for academic content, outlining the goals, objectives, and standards for evaluating students. Usually, a group of academics from a college curates and maintains it. A lecture or class can help one grasp the course curriculum being covered in greater detail. Both professors and students alike can obtain a thorough understanding of how to embrace the ideas covered in the coursework. A candidate's behaviour, understanding, abilities, achievement, and attitude are all outlined in the course curriculum. It focuses on various components of the teaching-learning process, including study materials, homework, tests, assignments, mental workouts, instructional strategies, learning goals, and presentations. Three main categories of curriculum exist, which are covered in the sections that follow:
Explicit Curriculum: Creating a carefully thought-out and organised curriculum with the learning purpose in mind is known as an explicit curriculum. It is often tested and reviewed as a pilot program before it's applied in educational facilities.
Hidden Curriculum: What pupils acquire throughout the teaching process is known as a hidden curriculum; it is not a component of a carefully thought-out and organised curriculum. Professors aim to instil values such as justice, honesty, etc. when they are teaching students.
Excluded or Null Curriculum: Null/ omitted course curriculum refers to the section of a course that a teacher sometimes chooses not to teach, whether on purpose or accidentally. They often come across some subjects or concepts that are unlikely to require in-depth explanations.
What is a Syllabus?
A syllabus unlike a curriculum is descriptive and focuses on the subjects to be taught for a particular academic session. It is determined and structured by an institution or an examination board that includes CBSE, ICSE, or any state boards. Each of the chapters and its respective topics or subtopics are mentioned to help learners grow a fundamental understanding of the subjects included in an academic year. The emphasis of the syllabus is enabling students to assimilate knowledge through the course material.
The syllabus is designed in collaboration with educators, board members, and teachers with a supreme objective to help students grasp the content easily. While selecting chapters and topics, the age of the learners is given relevance. During assessment, teachers ensure that questions are set per the syllabus pattern.
Difference Between Curriculum and Syllabus: Key Pointers
As you embark on your academic journey, you will frequently encounter the terms curriculum and syllabus. For students in various classes, streams, or educational boards, understanding what is the difference between curriculum and syllabus is essential, as outlined below:
Overview: The syllabus zooms in on a particular course or subject, whereas the curriculum covers the entire educational program.
Goals: The syllabus details topics, content, and learning objectives for a course, while the curriculum establishes broader educational aims.
Detail Level: The syllabus offers a specific instructional plan, while the curriculum shapes the overall design and structure of learning activities.
Specificity: The syllabus is more detailed, while the curriculum is more comprehensive and holistic.
Creation: The syllabus is crafted by individual teachers or departments, while the curriculum is formulated by educational institutions.
Components: The syllabus primarily highlights content and learning outcomes, whereas the curriculum encompasses content, teaching methods, and assessment strategies.
Updates: The syllabus can undergo frequent revisions based on changing needs, whereas the curriculum generally has a longer lifespan.
Timing: The syllabus is typically given to students at the course's start, while the curriculum acts as a framework throughout the program.
Focus: The syllabus serves as a guide for students and teachers, while the curriculum directs curriculum development and implementation at the institutional level.
Connection: The syllabus is a subset of the broader curriculum, which includes syllabi for various courses within an educational program.
Difference Between Curriculum and Syllabus: Developing a Syllabus
A syllabus acts as the model for teaching a course or subject that enables students to grasp a concept and achieve success in their academic term. When developing a syllabus, teachers or instructors take into account several factors including the purpose of teaching, the significance of a course, the age of learners, and topics to be taught for a course. Here are some of the steps undertaken for creating and developing a syllabus.
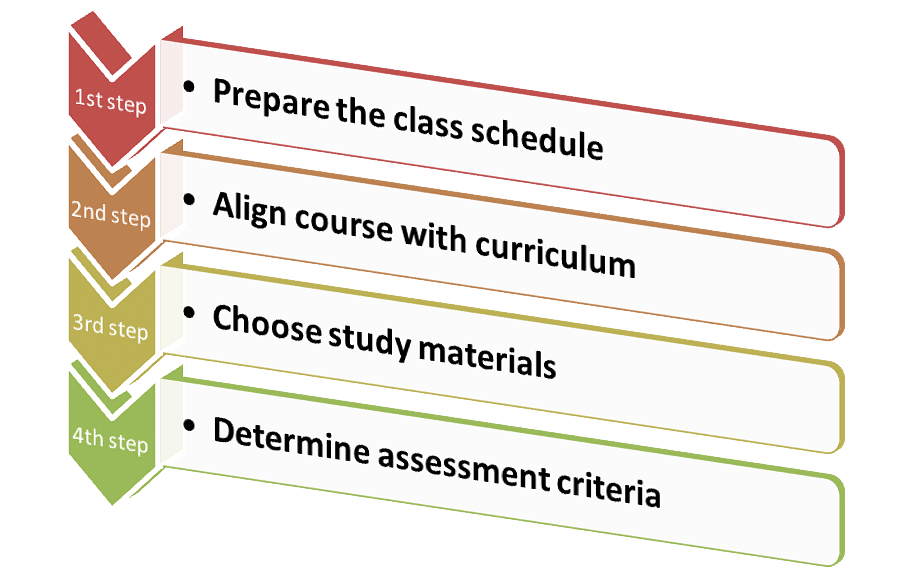
Prepare the class schedule: Educators responsible for designing the syllabus need to create a schedule to ensure that the course for a particular session is completed within a given time. Instructors can make a list of topics to be covered in ascending order or based on their importance.
Align course with curriculum: An important pre-requisite when curating a syllabus is to ensure that it perfectly fits the curriculum structure determined by the authorities of a school or college. Educators should decide on the type of course or level of learning necessary for the students.
Choose study materials: Choosing the right study material forms a crucial part of developing a syllabus. Educators have to determine which textbooks or study materials are required for students. Assessments are done based on suggested textbooks for a course.
Determine assessment criteria: Assessment is another significant part of syllabus creation. Be it the exams, class assignments, or projects, the syllabus must contain each of the details upon which learners will be tested.
Difference Between Curriculum and Syllabus: Designing a Curriculum
A curriculum unlike a syllabus offers a bigger picture of the education system hence its designing process is pretty vivid and extensive. When developing a curriculum three major components are considered including what to teach, how to teach, and who will teach. The process generally begins with the identification of issues related to teaching followed by a method of evaluation that can help in overcoming the problem. Find the process for designing a curriculum below:
Planning | Content and Method | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
Identifying a problem or concern | List the intended outcome | Develop curriculum |
Appointing a curriculum development team | Choose content | Assess and revise the curriculum |
Analysis of the need for assessment | Curate experiential methods | Recruit educators |
| - | - | Run a pilot project |
| - | - | Implement the curriculum |
Relationship Between Curriculum, Syllabus and Textbook
Now that we are pretty clear about what is the difference between curriculum and syllabus, let us discuss how it differs from academic textbooks. Since all of the three are integral parts of an academic session, their relationships are deeply interconnected. Let us explore this relationship in greater detail:
The curriculum lays forth the precise framework for the syllabus, class times, and suggested reading lists. All of the chapters and subjects are included in the curriculum, along with learning tools, reference materials, and extra academic guidelines. The textbook then adheres to the requirements specified in the syllabus and course curriculum for a semester or academic year.
A subject's lesson plans are included in the curriculum, but they are more in-depth than that because they are organised according to the syllabus's chapters and subjects, which are then covered in more detail by books.
A syllabus that is easier to understand and cover with the help of textbooks results from a more organised curriculum.
Academic writers and publishers construct textbooks per the curriculum and syllabus, which are developed by the education board, professors, and textbook manufacturers.
Textbooks differ depending on the syllabus for each academic session, such as a semester, and the curriculum, which covers a full school year, are the two main sources of information.
Having now elucidated what is the difference between curriculum and syllabus in detail. Let us also briefly discuss the parallels or their alikeness. There are several correlations between the syllabus and the curriculum.
Teaching is the only hidden agenda item for both.
They are both made under the government's specified requirements for education.
The entire development of students depends on both.
A course curriculum consists of two different parts, the syllabus and the curriculum. Making the distinction between these two ideas is crucial for professors as well as pupils to guarantee that academic objectives are satisfied and learning outcomes are attained. You ought to be well aware of the potential differences between a syllabus and a curriculum by this stage. Both ideas are essential to making sure you set yourself up for a successful educational path.
Related Articles:
| CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2023-24 | CBSE vs ICSE Board |
|---|---|
| ICSE Class 10th Syllabus 2023-24 | UP Board 12th Syllabus 2023-24 |
If you have any more queries concerning what is the difference between curriculum and syllabus, particular academic courses, entrance exams, or syllabus for UG or PG exams, you can post your question at CollegeDekho 's Q&A section or reach us at 1800-572-9877.
Are you feeling lost and unsure about what career path to take after completing 12th standard?
Say goodbye to confusion and hello to a bright future!

FAQs
The curriculum might be updated from time to time to align with shifts in educational standards, teaching methods, and societal requirements. These adjustments typically happen after thorough review and evaluation.
The syllabus can change more often. Pedagogues might update it every semester or academic year to adjust for changes in course content, teaching methods, and assessment techniques.
A curriculum acts as the learning blueprint, guiding teachers and students on a journey of knowledge and skill development. Its main purposes include:
- Structuring Learning: Outlining the crucial knowledge, skills, and values students should gain within a specific timeframe.
- Guiding Instruction: Providing teachers with a roadmap for effective lesson planning, teaching methods, and assessment strategies.
- Ensuring Equity: Promoting fairness and consistency by giving all students access to a standardized learning experience.
- Preparing for the Future: Equipping students with the necessary knowledge and skills to navigate future challenges and contribute meaningfully to society.
The syllabus serves three main purposes:
- Agreement: It outlines course expectations, assignments, grading policies, and student responsibilities, acting as a contract between the instructor and the student.
- Learning Guide: It provides a roadmap for the course, showcasing topics, schedules, and resources, guiding students through the learning journey.
- Reference: It documents course content, instructor information, and assessment methods, serving as a permanent record for both students and instructors.
Was this article helpful?




















Similar Articles
DU Colleges and Courses with Less than 90% Cut-Off Criteria
List of Colleges Accepting 5,000 to 10,000 Rank in TS ICET 2025
TS ICET 2025 Exam Day Instructions: Dos & Don'ts, Documents to Carry
List of Colleges Accepting Above 35,000 Rank in TS ICET 2025
How Many Times can I give 12th Board Exams?
Amravati FYJC 11th Admission 2025: Dates, Online Form, Merit List Junior College List, Process