- Thermodynamics - Thermal Equilibrium
- Thermodynamics - Definition of Temperature
- Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
- Thermodynamics - Heat, Work, And Internal Energy
- First Law of Thermodynamics
- Second Law of Thermodynamics
- Thermodynamics - Gaseous State of Matter
- Change of Condition of Gaseous State - Isothermal Process
- Thermodynamics - Adiabatic Process
- Thermodynamics - Reversible Process
- Thermodynamics - Irreversible Process
- Cyclic Processes in Thermodynamics

Thermodynamics refers to the study includes the flow of energy from one substance through another. The students will be able to learn about the transfer and the transformation of energy from one form to another through this unit. It is an equally important unit in their syllabus and they must have important knowledge related to the Thermodynamics units so that they can secure a good amount of marks. Check out the details related to the study notes for thermodynamics including the essential information on the first and the second law of thermodynamics given below with other important topics included in the curriculum:
Thermodynamics - Thermal Equilibrium
When the high temperature and the low-temperature balance out the heat stop flowing, and this system is known as Thermal Equilibrium. In a state of thermal equilibrium, it is said that there is no matter flowing into or out of the system.
Also Read:
Motion in a Straight Line
Thermodynamics - Definition of Temperature
Temperature is basically the quantity that can be measured through a thermometer. Basically, the intensity of heat that is present in a substance or an object measured through a comparative scale and shown through a thermometer is known as temperature.
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
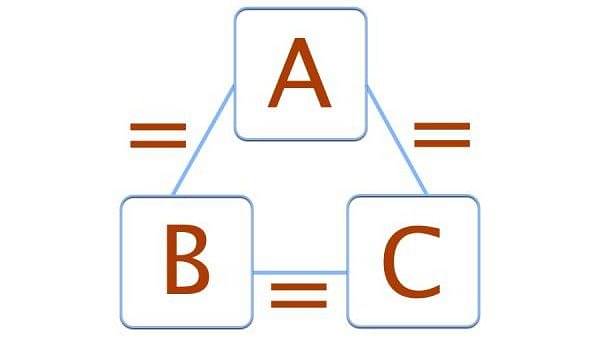
Thermodynamics consists of 4 laws and Zeroth's Law of Thermodynamics is among the four laws which are formulated by Ralph H. Fowler. The law is basically based on the measurement of the temperature between three bodies. When body ‘A’ is in thermal equilibrium with another body ‘b’, and also separately in thermal equilibrium with body ‘C’, then body ‘B’ and ‘C’ will also be in thermal equilibrium with each other. This statement defines the zeroth law of thermodynamics.
Thermodynamics - Heat, Work, And Internal Energy
Heat is a form of energy when one energy is transferred from one system to another. Internal energy is the energy contained within the system associated with random motions of the particles along with the potential energies of the molecules due to their orientation. The energy due to random motion includes translational, rotational, and vibrational energy. It is represented as U. Work done is the total amount of energy that the system and its surrounding exchange within itself.
Formula For Internal Energy
ΔU = Q + W
Where,
ΔU is the internal energy
Q is the heat added to the system
W is the work done by the system
Formula For Work
W = ∫P.dV
First Law of Thermodynamics
The first law of thermodynamics clearly states that energy cannot be created or destroyed however it can be transferred from one location to another and converted from one type of energy to the other type of energy. It states that heat is a form of energy, and thermodynamic processes are therefore subject to the principle of conservation of energy.
Formula For First Law of Thermodynamics
ΔU = q + W
Where
ΔU = change in internal energy of the system.
q = algebraic sum of heat transfer between system and surroundings.
W = work interaction of the system with its surroundings.
Exceptions For First Law of Thermodynamics
Some of the exceptions for the first law of thermodynamics are present below to be considered while using the equation:
- Energy will always remain constant for an isolated system.
- Internal Energy is a point function and property of the system. Internal energy is an extensive property (mass-dependent) while specific energy is an intensive property (independent of mass).
- For an ideal gas, the internal energy is a function of temperature only.
Second Law of Thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics states that any spontaneously occurring process will always lead to an escalation in the entropy (S) of the universe. It explains that it is impossible to convert heat energy into mechanical energy with 100% efficiency. In simple words, it means that when the energy is transformed or transferred then more of it is wasted.
Formula For Second Law of Thermodynamics
ΔSuniv > 0
where ΔSuniv is the change in the entropy of the universe.
Second Law of Thermodynamics - Kelvin-Planck Statement
It is impossible for a heat engine to produce a network in a complete cycle if it exchanges heat only with bodies at a single fixed temperature. If Q2 =0 (i.e., Wnet = Q1, or efficiency=1.00), the heat engine produces work in a complete cycle by exchanging heat with only one reservoir, thus violating the Kelvin-Planck statement.
Second Law of Thermodynamics - Clausius’s Statement
Clausius' Statement states that it is impossible to construct a device that is operating in a cycle to transfer heat from a cold body to a warm body without consuming any work. The flow of energy is not spontaneous from a lower-temperature object to a higher-temperature object.
Thermodynamics - Gaseous State of Matter
A state of matter which does not have any fixed shape or fixed volume is known as a gas. Because it has a lower density as compared to the other states of matter such as solids and liquids, there are a lot of empty spaces between the particles and a lot of kinetic energy is present. The particles are not particularly attracted to one another.
Characteristics of Gaseous State of Matter
There are a lot of characteristics that will help you to identify the gaseous state of matter. Check out the characteristics from the pointers given below:
- Gas has a lower density and it is compressible as compared to the solids and liquid state of matter.
- In a gaseous state, there is an equal amount of pressure in all directions.
- The space between the gas particles is high and they have high kinetic energy also.
- There is a negligible intermolecular force between the particles in a gaseous state of matter.
- The particles move at a high speed in all directions and they also hit each other which causes the gas to spread throughout the container evenly and this also exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
- The gaseous state of matter can easily take the volume and shape of the container in which it is.
Change of Condition of Gaseous State - Isothermal Process
Isothermal literally translates to the word constant temperature. The definition of the isothermal process is a thermodynamic process which is occurring at a constant temperature.
Examples of Isothermal Processes
There are a lot of day-to-day examples of isothermal processes. Check out some of the examples from the pointers given below:
- When the physical change in liquid is observed the procedure which takes it into account is the isothermal procedure. This includes evaporation and melting.
- The working of a rest fridge rate is also an isothermal process because the temperature inside the refrigerator remains constant and the heat energy is removed by transmitting it to the surrounding environment.
- AC is also another example of an isothermal process because the heat from the room is removed and dumped outside the house. The main goal is to keep the temperature inside the house according to the needs of the customers.
Also Read:
Thermodynamics - Adiabatic Process
Adiabatic means isolated from surroundings and the definition of an adiabatic process means the process in which the heat is not allowed to transfer inside or outside the system.
Formula For Adiabatic Process
PVγ = constant
Here P stands for the pressure of the system
V stands for the volume of the system
γ stands for adiabatic index
Examples of Adiabatic Process
There are several instances of the Adiabatic process. Check out some of the examples given below:
- One of the most simple processes which include Adiabatic conversion is the release of air from a pneumatic tire.
- Adiabatic Process is also present in the efficiency which is applied in nozzles, compressors, and turbines.
- When the pendulum oscillates in a vertical plane then also it is an example of the Adiabatic Process.
Thermodynamics - Reversible Process
A reversible process is a procedure in which the system and the environment can be restored to exactly the same state which was present before the procedure occurred if you are going toward the past state. The necessary condition for a reversible process is therefore the quasi-static requirement. The possibility of a reversible process is very low.
Thermodynamics - Irreversible Process
The reversible process is a very normal process that is counter in reality all the time in this processor the system and the environment cannot be restored to their original state at the same time. The other name for the reversible process is the natural process. The phenomenon in which the past state of the substance is not achieved after the proper procedure is known as irreversibility.
Cyclic Processes in Thermodynamics
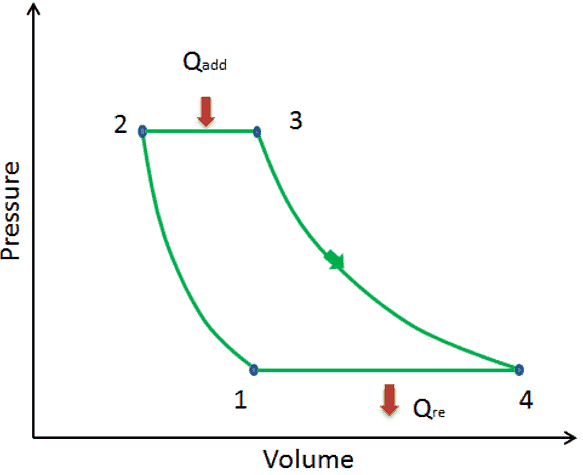
When a system returns to its initial state after a process, this process is called a cyclic thermodynamic process. The initial and the final state of the matter are the same in a cyclic procedure. The total change in the internal energy of the system is zero in a cyclic procedure. Heat engines work in a cyclic process.
Formula For Cyclic Processes in Thermodynamics
ΔE = Q+W
Where, ΔE = 0, W = Q
Thermodynamics is one of the most important units which will be present in Physics subject of class 12th board examination 2023. Check out the specifications related to the study notes for the unit from the article shared above and prepare yourself accordingly.
Are you feeling lost and unsure about what career path to take after completing 12th standard?
Say goodbye to confusion and hello to a bright future!

Was this article helpful?

















Similar Articles
Gujarat University B.Ed Admission 2025: Important Dates, Application Form, Eligibility, Counselling Process
VMOU B.Ed Admission 2025: Exam Date, Registration, Syllabus, Admit Card, Result, Counselling
Haryana B.Ed Admission 2024: Dates, Application Form, Eligibility Criteria, Merit List, Counselling Process, Seat Allotment
Rajasthan B.Ed Admission 2025
Indira Gandhi University B.Ed Admission 2025: Dates, Application Form, Eligibility, Process
Assam TET 2024: Answer Key (Out), Admit Card (Out), Dates (Out), Application Form, Syllabus, Result, Selection Process