Last Updated By Subhashri Roy on 14 Aug, 2023
If you have an aptitude for finances, mathematics, and management, and believe you can manage consumers well, you may aspire to become a Bank Manager. The executives at the bank have a lot of faith in the Bank Manager and expect them to operate their branches like their own companies. Virtually every aspect of a branch's operations is under the purview of a Bank Manager, including expanding the area's customer base and improving the perception of the company's brand in the neighbourhood. The success or failure of the branch they oversee lies on the bank manager. In order to complete duties in a timely and effective manner, excellent multitasking and organizational abilities are required to become a Bank Manager.

Bank managers act as the face of the bank in their local community. They provide investment and saving-related advice to customers. A good Bank Manager should have expert knowledge of every aspect of the bank’s operations. They should have the ability to handle multiple tasks at the same time. It's critical to comprehend what this position comprises and the courses you may take in this domain while thinking about how to become a Bank Manager. Consequently, we will go into detail about the essential elements of bank management and how to become a Bank Manager below.
An individual who is responsible for managing a bank or other financial institution's branch is known as a Bank Manager. Bank Managers supervise a group of bank staff members, such as tellers, customer care agents, loan officers, and other staff members. Most bank managers hold bachelor's degrees in finance, accounting, or closely related disciplines of study. Bank Managers are in charge of overseeing the financial performance of the branch. Setting and achieving financial goals, keeping an eye on revenues, expenditures, and profits, and taking the necessary steps to ensure financial stability are all responsibilities of a Bank Manager.
The delivery of exceptional customer service is a key focus. In addressing customer complaints, resolving customer issues, and preserving an excellent relationship with customers, you should be proactive. The position of Bank Manager includes actively promoting the development of the business. They collaborate with their teams to identify sales opportunities, promote banking goods and services, and bring in new clients while maintaining current ones. Bank Managers also conduct evaluations of performance, provide feedback and put initiatives into place to boost productivity among staff members.
A combination of education, experience, and specific skills must be understood by the candidates to know how to become a Bank Manager.
In India, there is no specific exam designated solely for the purpose of becoming a bank manager. However, students majoring in commerce can apply to any reputable institution in India by taking one of a number of entrance exams mentioned below:
To become a Government Bank Manager in India, you generally need to qualify through competitive exams conducted by various banking organizations or government agencies. Here are the key exams conducted for government bank manager positions in India:
IBPS Probationary Officer (PO) Exam: The IBPS PO exam is conducted by the Institute of Banking Personnel Selection (IBPS) to recruit Probationary Officers in multiple public sector banks. Selected candidates join as Assistant Managers and can progress to managerial roles based on their performance and experience.
IBPS Specialist Officer (SO) Exam: The IBPS SO exam is held to recruit candidates for specialist positions like IT Officer, Marketing Officer, Law Officer, and others. Specialist Officers can also advance to managerial positions based on their performance and experience.
SBI Probationary Officer (PO) Exam: The State Bank of India (SBI) conducts its own PO exam for recruiting Probationary Officers. Successful candidates become Assistant Managers and can grow into managerial roles through the SBI PO Exam.
SBI Specialist Cadre Officer (SO) Exam: SBI conducts specialized recruitment exams for various Specialist Cadre Officer positions, such as IT Officer, Relationship Manager, Credit Analyst, etc. These roles can lead to managerial positions.
Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) Exam: IBPS conducts separate exams for Officer Scale-I, II, and III positions in Regional Rural Banks (RRBs). Candidates who clear these exams and are selected as Officer Scale-I (Assistant Manager) can progress to higher managerial roles.
To prepare for these exams, candidates must be well-versed in banking and financial concepts, current affairs, general awareness, reasoning, and quantitative aptitude. Regular practice, solving previous year question papers, and mock tests are essential for success in these competitive exams.
Here are some key skills and attributes that are important for aspiring bank managers:
Becoming a Bank Manager abroad typically follows a similar path as becoming a bank manager in India. To become a Bank Manager abroad, candidates must obtain a relevant bachelor's degree in finance, business administration, economics, accounting, or a related field. Some countries may require additional qualifications, such as a master's degree or specific certifications.
Aspiring Bank Managers may work in the banking industry to gain experience and advance their career. Starting from an entry-level position, such as a bank teller or customer service representative, can provide them with valuable experience and opportunities for promotion. Candidates must consider specializing in a particular area within the banking industry, such as retail banking, corporate banking, investment banking, risk management, or wealth management.
The exams required to become a bank manager abroad can vary depending on the country's banking regulations, the specific bank or financial institution, and the level of the managerial position. However, some common exams or certifications that may be valuable for aspiring bank managers abroad include:
In addition to specific exams, having relevant educational qualifications, banking experience, leadership abilities, and a commitment to continuous learning can contribute to your success as a bank manager abroad. Networking, professional development, and a willingness to adapt to different cultural environments are also important factors to consider when pursuing a career as a bank manager in another country.
Here are some key skills and attributes that are important for aspiring bank managers abroad:
One cannot become a Bank Manager directly after completing their 12th standard exams. Becoming a Bank Manager typically requires higher education and relevant work experience. After completing 12th grade (10+2), you can follow these steps to work towards becoming a Bank Manager:
Here are the steps you can take to work towards becoming a Bank Manager after completing your graduation.
Becoming a Bank Manager after Graduation does not require appearing for entrance exams. However, candidates aspiring to pursue a Master's in Business Administration (MBA) must appear for the following entrance exams:
When candidates have acquired substantial work experience and demonstrated their leadership and managerial capabilities, they may start applying for Bank Manager positions within the organization or in other banking institutions.
The qualifications of Bank Manager can vary depending on the bank's policies, the level of the managerial position, and the local regulations. Here are some common qualifications of Bank Manager that candidates must understand to know how to become a Bank Manager:
Bank Manager Qualifications Particulars | Eligibility Criteria |
Education Required |
|
Work Experience |
|
Certificates Required |
|
Physical abilities are generally not a primary consideration for the position of a Bank Manager, as the role primarily involves managerial, leadership, and administrative responsibilities. However, like any professional job, bank managers should possess good overall health and well-being to effectively carry out their duties. The general physical requirements for Bank Manager include the following:
Bank managers can hold different types of positions and responsibilities within a bank, depending on the size of the branch, its organizational structure, and the specific functions they oversee. Here are some common types of bank managers.
A branch manager is in charge of managing the operations of a certain bank branch. They oversee the branch's employees, guarantee top-notch customer service, achieve financial goals, and uphold adherence to banking rules and regulations.
Relationship managers focus on building and maintaining relationships with high-value clients, businesses, or corporate customers. They provide personalized financial solutions and act as a point of contact between the bank and their clients.
Credit managers are responsible for managing the bank's lending operations. They assess loan applications, determine creditworthiness, set lending terms, and monitor loan portfolios. Treasury managers manage the bank's liquidity and financial assets. They oversee cash management, investment activities, and funding strategies to ensure the bank's financial stability.
Business development managers are responsible for identifying and pursuing new business opportunities for the bank. They work on expanding the bank's customer base and market presence. They work closely with their sales staff to create ideas that are advantageous to both parties, negotiate the conditions of contracts, and effectively communicate with stakeholders.
A Certified Management Accountant (CMA) is a financial professional who has demonstrated proficiency in management accounting, financial analysis, and strategic decision-making. CMAs are well-versed in areas such as budgeting, cost management, performance evaluation, and risk management. They play a crucial role in helping organizations make informed business decisions and achieve financial goals.
There are two types of Bank Managers i.e Retail bank managers and Commercial bank managers. The Retail bank managers manage the transactions involving in various bank branches across the country. On the other hand, Commercial bank managers deal with medium-sized enterprises and small companies and provide them with banking and financial services to increase their business. Most of the operations of Retail bank managers are carried via phone or internet. There are many other profiles available for a Bank Manager. Some of them are provided below:
Branch Manager
Financial Planner
Mortgage Broker
Service Manager
If you want to know what occupation is right for you, you can take our Career Profiling Test. Besides this, you can ask questions about a career as a Bank Manager on Collegedekho QnA zone
Bank Managers may look for a job at any financial institution such as Investment Banks, Commercial Banks, or Brokerages. Besides this, he can also look for a job at any Consultancy or Insurance Company. The graph provided below will help you know different types of companies and areas where a Bank Manager can apply for a job.
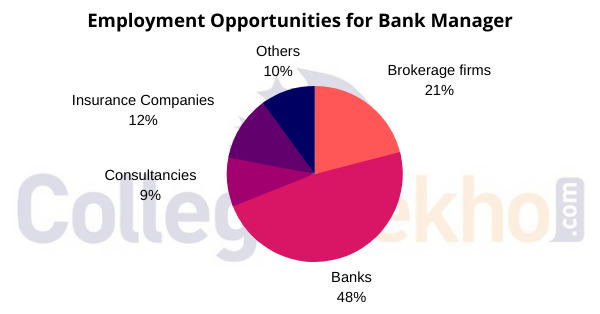
Some of the major recruiting companies for Bank Managers are listed below:
State Bank of India
ICICI Bank
HDFC Bank
Axis Bank
Kotak Mahindra Bank
Bank of Baroda
IndusInd Bank
YES Bank
IDBI Bank
The salary of bank managers in India can vary based on several factors, including the type of bank, the size of the branch, the manager's experience, and the location of the branch. Here are some approximate salary ranges for bank managers in India:
Profile | Mid Level Salary per annum (in INR) | Senior Level Salary per annum (INR) |
Junior Bank Manager | 7,84,000 | 10,00,000 |
Mid-Level Bank Manager | 6,80,000 | 20,00,000 |
Senior Bank Manager | 13,70,651 | 30,00,000 |
On average, the salary of a financial planner in India can be as follows:
On average, the salary of a Credit Manager can be as follows:
On average, the salary of a Relationship Manager in India can be as follows:
On average, the salary of a Certified Management Accountant (CMA) in India can be as follows:
To become a Bank Manager, you can pursue a bachelor's/master’s degree in a relevant field that provides a strong foundation in finance, banking, or business administration. Here are some common bachelor's and master’s degree courses that can help you work towards becoming a Bank Manager.
Bachelor’s Degree Courses |
|
Master’s Degree Courses |
|
Certification Courses |
|
Check the table below to know which colleges provide the courses required to become a Bank Manager.
Courses | Names of Colleges |
B.Com in Banking and Finance | |
MBA in Banking and Finance |
Provided below are some recommended books on how to become a Bank Manager:
The Bank Manager by Roger Monk
Learning by Example by David Strang
Commercial Bank Management by Benton E Gup
Bank Management by Timothy W. Koch
Credit Risk Measurement by Anthony Saunders and Linda Allen
An Introduction to Banking by Moorad Choudhry
Commercial Bank Financial Management by Joseph F Sinkey
One of the major benefits of becoming a Bank Manager is a good salary.
You will have fixed working hours. You do not have to work during weekends.
This profile will help you stay updated with the latest technologies in banking and finance
This profile is perfect for the candidates who are good in finance and accounting
There is strong competition for this position
At least 3 years of work experience is required
You should good leadership and management skills
You will be responsible for resolving the complaints of customers
Take our test and find out if it suits your strengths.

You may start as a probationary officer, and after a few years of experience and performance, you may be promoted to roles like Assistant Manager, Relationship Manager, or Officer, depending on the bank's hierarchy. After several years of experience in mid-level positions, you may be promoted to Associate Manager or Deputy Manager. The next step is becoming a full-fledged Bank Manager, which can be achieved after gaining significant experience, usually 5 to 10 years, and consistently demonstrating leadership and management abilities.
Yes, you can give some bank exams after completing your 12th (higher secondary) education. However, please note that most of the major banking exams for officer-level positions typically require candidates to have completed their graduation (a bachelor's degree) as the minimum educational qualification. The banking exams you can consider after 12th include the State Bank of India (SBI) Junior Associate (Clerk) Exam and the Institute of Banking Personnel Selection (IBPS) Clerk Exam.
The degrees that are commonly considered beneficial for becoming a Bank Manager include Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com), Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA), Bachelor of Science (B.Sc) in Banking and Finance, Master of Business Administration (MBA) in Banking and Finance, Master of Science (MSc) in Finance or Banking, etc.
Some of the common banking exams conducted for the position of Bank Manager include:
Becoming a Bank Manager can be challenging, but it is also a rewarding and fulfilling career path for individuals with the right qualifications, skills, and determination. Bank managers are accountable for meeting targets, achieving financial goals, and ensuring the branch's success. The pressure to deliver results can add to the challenges of the role. Bank managers may have demanding work schedules, especially in larger branches or during busy periods. Balancing various responsibilities, such as employee management, customer service, and administrative tasks, can be demanding.
A minimum of a bachelor's degree is essential for becoming a Bank Manager. While there is no specific degree requirement to become a Bank Manager, degrees in finance, business administration, economics, accounting, or related fields are commonly preferred. While not mandatory, some Bank Managers may hold a master's degree in business administration (MBA) with a specialization in finance or banking.
Major recruiters for bank managers include:
Some of the other profiles available for a Bank Manager are Mortgage Broker, Branch Manager, Relationship Manager, Financial Planner, Retail Banking Manager, Credit Manager, Marketing Manager, Service Manager and Chartered Accountant. Branch managers are responsible for the overall operations of a bank branch. They oversee customer service, business development, staff management, and ensure the branch meets its financial targets. Relationship managers work closely with high-net-worth individuals (HNIs) or corporate clients to understand their financial needs and provide personalized banking solutions and investment advice.
Becoming a successful bank manager requires a combination of technical, managerial, and interpersonal skills. Some essential skills that are required to excel in a bank manager role include banking and financial Knowledge, leadership and management, customer service, sales and business development, communication skills, financial analysis skills, and team building skills.
The salary of a Bank Manager varies depending on his skills and experience. Bank managers in public sector banks typically make around Rs. 50,000 to Rs. 80,000 per month, including basic pay, allowances, and benefits. In private sector banks, bank manager's salary in private banks can range from Rs. 8 lakh to Rs. 20 lakh per annum. The salary of Bank Managers in Foreign Banks can range from Rs. 12 lakh to Rs. 25 lakh per annum, depending on the level of the managerial position and the bank's policies.
The Bank Manager of a bank plays a crucial role in managing the day-to-day operations of a bank branch and ensuring its smooth functioning. The Bank Manager is responsible for overseeing all activities and operations at the branch, including cash management, customer transactions, account opening, and ensuring compliance with banking regulations. Branch Manager is accountable for driving business growth by promoting and selling various banking products and services.