KCET 2023 Physics Questions
Candidates can check the KCET 2023 Physics questions along with the answers here.
1. In a permanent magnet at room temperature
- a. Domains are all perfectly aligned.
- b. The magnetic moment of each molecule is zero.
- c. The individual molecules have non-zero magnetic moments which are all perfectly aligned.
- d. Domains are partially aligned.
Answer: A
Due to thermal agitation, with an increase in temperature randomness of the molecules increases and magnetic field moments get partially aligned. Hence the domains are partially aligned.
2. A rod of length 2 m slides with a speed of 5 ms-1 on a rectangular conducting frame as shown in the figure. There exists a uniform magnetic field of 0.04 T perpendicular to the plane of the figure. If the resistance of the rod is 3Ω then the current through the rod is
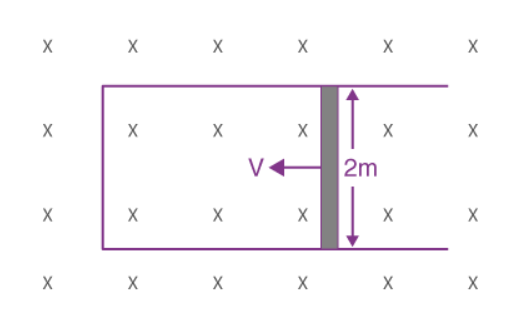
- a. 1.33 A
- b. 75mA
- c. 133 mA
- d. 0.75 A
Answer: C
We know that the current, i = Blv/R= (0.04×2×5)/3 = 133 mA
3. The ratio of the magnetic field at the center of a current-carrying circular coil to its magnetic moment is ‘x’. If the current and the radius both are doubled then the new ratio will become
Answer: A
The magnetic field at the center of the current carrying loop is given by B=(μ0/4π)×(2πi/a)=(μ0 i)/2a.
The magnetic moment at the center of the current carrying loop is given by M=iπa2
thus B/M=μ0/(2πa3 )=x (given) when both current and radius are doubled ratio becomes x/8 times.
4. The current in a coil of inductance 0.2 H changes from 5 A to 2 A in 0.5 sec. The magnitude of the average induced emf in the coil is
- a. 0.3 V
- b. 0.6 V
- c. 1.2 V
- d. 30 V
Answer: c
Average induced emf, ϵ=L dI/dt
=0.2 ((5-2)/0.5)=(2/5) × 3=1.2 V
5. Three polaroid sheets P1, P2, and P3 are kept parallel to each other such that the angle between the pass axes of P1 and P2 is 450 and that between P2 and P3 is 450. If an unpolarised beam of light of intensity 128 Wm-2 is incident on P1. What is the intensity of light coming out of P3?
- a. 64Wm-2
- b. 128 Wm-2
- c. 0
- d. 16 Wm-2
Answer: D
We have unpolarised beam’s intensity I0=128w/m2
Using Malu’s law we have I=I0 cos2 θ
When the beam passed from the first polaroid, I=I0/2
Again, as the angle between p1 and p2 is 450, beam intensity when it will pass p2 would be I1=I0/2 cos2450=I0/4
And, also the angle between p2 and p3 is 450, and beam intensity when it comes out of p3 will be I2=I0/4 cos2 450=I0/8=128/8=16w/m2
6. Two poles are by a distance of 3.14 m. The resolving power of the human eye is the minute of an arc. The maximum distance from which he can identify the two poles distinctly is
- a. 376 m
- b. 10.8 km
- c. 5.4 km
- d. 188 m
Answer: B
Given the lateral separation of the poles d=3.14 m
The resolving power of the eye is θ=1min=π/(60×180) rad
The maximum distance from which poles are distinctly visible is D=d/θ
⇒D=(3.14×60×180)/π=10800m=10.8 km
7. The following figure shows a beam of light converging at point P. When a concave lens of focal length 16 cm is introduced in the path of the beam at a place shown by a dotted line such that OP becomes the axis of the lens, the beam converges at a distance x from the lens. The value of x will be equal to

- a. 48 cm
- b. 12 cm
- c. 24 cm
- d. 36 cm
Answer: a
So, here when we put the concave lens, let the beam converge at a distance of x=v
Using lens formulae, we have, 1/f=1/v-1/u
Where u=12 cm and f=-16 cm is given
∴1/v=(1/f)+(1/u)=(-1/16)+(1/12)=1/48 cm⇒ v=48 cm
Hence, x=48 cm
8. The de-Broglie wavelength associated with the electron of a hydrogen atom in this ground state is
- a. 10A0
- b.0.3Ao
- c. 3.3Ao
- d.6.26Ao
Answer. C
De-Broglie wavelength is given by λ=12.27/√E0, where E0 is the ground state energy of the hydrogen atom whose value is 13.6 V
∴λ=12.27/(√1 3.6)=3.33 Ǻ
9. The de-Broglie wavelength associated with the electron of a hydrogen atom in this ground state is
- a. 10A0
- b.0.3Ao
- c. 3.3Ao
- d.6.26Ao
Answer. C
De-Broglie wavelength is given by λ=12.27/√E0, where E0 is the ground state energy of the hydrogen atom whose value is 13.6 V
∴λ=12.27/(√1 3.6)=3.33 Ǻ
10. In Young’s Double Slit Experiment, the distance between the slits and the screen is 1.2 m and the distance between the two slits is 2.4 mm. If a thin transparent mica sheet of thickness 1μm and R.I of 1.5 is introduced between one of the interfering beams, the shift in the position of the central bright fringe is
- a. 0.25 mm
- b. 2 mm
- c. 0.5 mm
- d. 0.125 mm
Answer: A
Path difference due to insertion of mica sheet Δx=(μ-1)t
Let the shift in the fringe pattern be 'y'
Also, path difference Δx=y×d/D, so comparing both (μ-1)t=y×(d/D)
y=(μ-1)t×(D/d) , where μ=1.5,D=2.4 and d=1.2 putting the values, we get
y= 0.25 mm.











