BODMAS full form is Bracket, Order, Division, Multiplication Addition, and Subtraction, and it’s a rule in mathematics helping students solve mathematical problems easily. Basically, with the help of this rule, children can solve complex equations that comprise different functions like division, subtraction, order, bracket, multiplication and addition. BODMAS enables setting the right order to solve a mathematical problem that eliminates the occurrence of any mistake.
As mentioned above, BODMAS full form is Bracket Order Division Multiplication Addition and Subtraction. Solving equations that require you to use all the mathematical functions like multiplication, subtraction, division, etc. can be easily done with the BODMAS rule. Calculations are carried out from left to right.
Similar to BODMAS another rule called PEMDAS is also widely used for solving equations. PEMDAS full form is Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication, Division, Addition and Subtraction. Schools generally use the BODMAS rule in the primary sections to help small children to get acquainted with solving mathematical problems with ease. If you are lately confused regarding this amazing rule, we suggest you read our article to gather information on BODMAS, its principles and importance.
BODMAS full form | Bracket Order Division Multiplication Addition and Subtraction |
|---|---|
Invented by | Achilles Reselfelt, |
Uses | To solve complex mathematical equations |
Benefit | Helps simplifying problems that incorporates all the mathematical operations |
Taught to | School children |
As per BODMAS, a particular order is followed when solving complex equations that involve different mathematical operations. When performing all the operations like bracket, multiplication, addition, subtraction, order and division, you have to solve them using a specific order. You need to begin with solving the bracket first, then move ahead to order that relates to solving power or roots, and further proceed to division, multiplication, addition and lastly subtraction to get the right result.
In fact, for solving brackets that sometimes consist of the first, second or third bracket, in this case, try to simplify terms inside brackets starting from the innermost brackets, and moving to the outer ones. Below we have represented the rule in a table format.
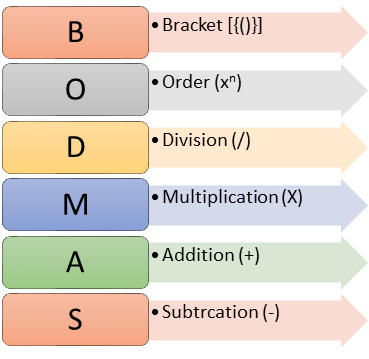
Figure1: BODMAS Rule
BODMAS follows a particular order from left to right while solving any complex equation in mathematics. Well, each of the components or functions in this rule is based on certain conditions that you will understand in this section.
Learn the tips thoroughly to solve a mathematical equation involving addition, subtraction, bracket, division, multiplication and order appropriately.
Rule 1: Start with the brackets first, move from solving numbers in the innermost bracket, and gradually move to the outer ones
Rule 2: Next, move ahead with the roots or exponents in the equation
Rule 3: Perform division and multiplication one by one (left to right)
Rule 4: Finally, do the addition and subtraction to get the correct answer (left to right)
B | Brackets | (), {}, [] |
|---|---|---|
O | Order of | Square roots, indices, exponents and powers |
D | Division | ÷, / |
M | Multiplication | X |
A | Addition | + |
S | Subtraction | - |
Lets help you understand the BODMAS rule with an example.
(6+8)-4+2
To solve this equation you need to first begin with solving the bracket
(14)-4+2
As per rule, next you should solve the addition
(14)-6
Lastly, subtract it
(14)-6=8
Application of the BODMAS rule has certain exceptions; you can’t use the rule in every mathematical equation. While solving an equation that includes only one particular operation, the BODMAS rule is not applicable. This mathematical rule suits an equation that expects you to inculcate all the major operations, in such cases, the BODMAS rule is mandatory. For any confusion, take guidance from your math teacher so you get correct answers.
When solving an equation using the BODMAS rule, open needs to adhere to certain conditions that are mentioned below.
Conditions | Rules |
|---|---|
x+(y+z) = x+y+z | Open bracket and add the terms |
x-(y+z) = x-y-z | Open bracket nd multiply negative signs with each term inside the bracket |
x(y+z) = xy+xz | Multiply the outside numericals with each trem inside the bracket |
In today’s time, solving complex mathematical operations that involve all the operations, can be easily solved with the BODMAS rule. Do you wish to discover the person behind this wonderful invention? BODMAS was invented by the mathematician Achilles Reselfelt; well, there is no evidence of the actual year of its invention.
His primary objective was to simplify solving complex equations by remembering which operation to do first by remembering it with their first alphabet. Before BODMAS, another similar rule called PEMDAS was also used by people to solve mathematical problems with ease. However, BODMAS is taught in schools to help children become acquainted with solving problems in a better way.
BODMAS is a mathematical rule applied in equations that require varied functions; hence, mistakes are fairly commonplace. When solving an equation with multiple functions, children stumble upon remembering the correct order of operations. One of the major issues a student faces is finding the right way to solve multiple brackets.
It is advised to take special care of the sequences that include brackets followed by order, division, multiplication, addition and subtraction. At times, limited clarity in understanding the subtraction and addition of numbers creates difficulties in getting the right answer.
For example in the equation
3-6+7 = -3+7=3
However, if we put it in the following manner
3-6+7 = 3-13= -10, it will be wrong answer
Students need to clarify the fact that multiplication and division are almost at the same level of operation so when solving any equation, functions should be performed from left to right. Similar strategy is prevalent in solving subtraction and addition.
Suppose, if a student begins with solving the division before multiplication only because D is before M in BODMAS, the answer will be wrong.
Let’s solve one question on BODMAS rule to make it clear for students so that they can avoid any sort of mistakes
Solve 8+9/9+5*2
In this case, start solving the division first i.e. 9/9=1
Therefore, 8+1+5*2-7
Now multiply 8+1+10-7
Perform addition first 19-7= 12
So, the result will be 12.
It won’t be wrong to say that the BODMAS rule forms the foundation of applied mathematics. Without using this rule, students will face issues in devising the right way to solve complex mathematical equations. Well, not even equations mentioned in your math book require the application of BODMAS because it is used only in problems that expect you to use operations like division, order, bracket, multiplication, subtraction and addition.
As a general rule, schools introduce students to BODMAS before beginning with algebra. Students need to learn this rule and remember the correct order to solve mathematical equations to get the correct answer. Mastering the BODMAS rule can help in underpinning difficult mathematical problems easily.
So, you must have gained subsequent ideas regarding the use of the BODMAS rule and how vital role it plays in helping people solve complex equations easily. In case, you still follow a haphazard sequence in solving the equation, you will definitely end up with wrong answers. Therefore, it is necessary to learn this easy and amazing concept to complete any equation without making any mistakes.
The full form of BODMAS is Bracket Order Division Multiplication Addition and Subtraction and is used to solve complex equations.
Yes, BODMAS forms an integral part of mathematics as it helps in solving complex problems easily.
BODMAS is applicable in mathematical equations that expects you to use all the operations like bracket, multiplication, subtraction, addition, order and division.
BODMAS was invented by mathematician Achilles Reselfelt.
Before introducing the chapter on algebra schools generally teaches BODMAS rule to school children.